Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Gold (XAU/USD) has returned to a well-defined range on Wednesday, as markets continue to show signs of optimism following Tuesday’s ceasefire between Israel and Iran.
At the time of writing, Gold is holding above $3,300 as markets digest the latest release of US macroeconomic data and remarks made on the second day of testimony from Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell.
With tensions in the Middle East appearing to remain subdued, Wednesday’s economic data releases and comments from Powell have served as an additional catalyst for Bullion.
US New Home Sales data for May, released at 14:00 GMT, fell below expectations, indicating that the housing market may be coming under pressure. Analysts had anticipated the May report to show 690,000 single-family homes sold. The actual figures showed 623,000 units sold, while the monthly percentage change declined 13.7%, a sharp decrease from the prior 9.6% increase.
Meanwhile, Jerome Powell continues to speak before the US Senate Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs, where any shift in tone or mention of inflation risks could drive interest rate-sensitive assets, including Gold. So far, Powell has remained optimistic about the resilience of the US economy, despite the risks posed by high interest rates and weaker economic data.
Gold price is currently trading above the key psychological support level of $3,300, with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator flattening near the 48 mark on the daily chart, suggesting a lack of momentum and indecision among traders.
At the time of writing, XAU/USD is trading in line with the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA), at $3,325.
Gold (XAU/USD) daily chart
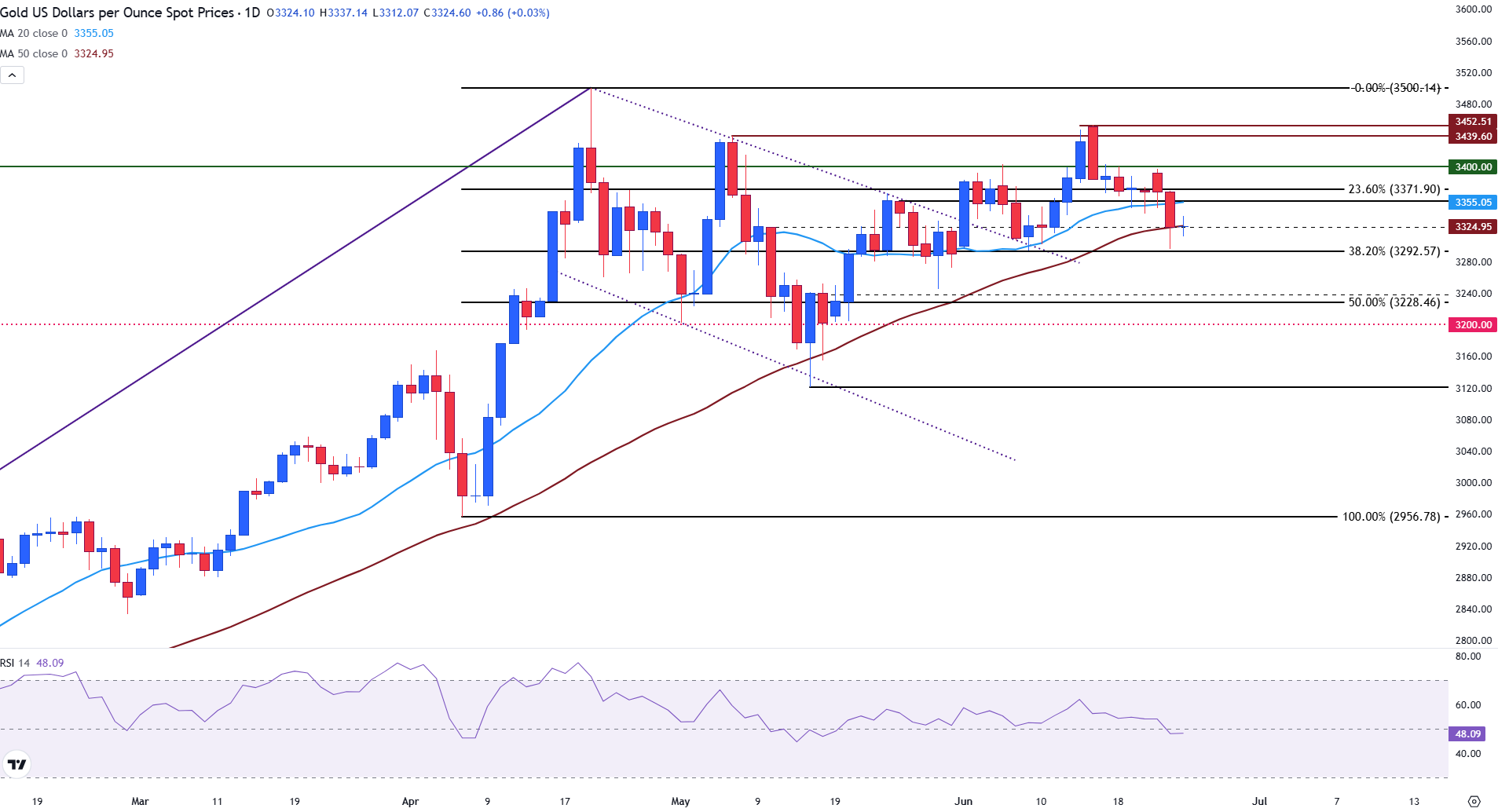
For the price to extend its recovery, a move above the 20-day SMA at $3,355 is required. If bulls succeed in clearing this barrier, the next level of resistance will likely reside at the $3,400 psychological level.
However, if risk appetite improves, demand for safe havens could continue to decline in the short term. If the Gold price faces a deeper pullback below the $3,300 round level, the midpoint of the rally from the April 7 low to the April 22 high (the 50% Fibonacci retracement level) could come into play as support at $3,228.
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates.
When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money.
When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions.
The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system.
It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.