Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Gold price (XAU/USD) struggles to capitalize on modest intraday gains on Wednesday, though it manages to hold comfortably above the $3,300 mark and over a two-week low touched the previous day. The optimism over the Israel-Iran ceasefire remains supportive of the positive risk tone and acts as a headwind for the safe-haven precious metal. Adding to this, the emergence of some US Dollar (USD) buying, bolstered by Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell’s hawkish remarks on Tuesday, turns out to be another factor capping the non-yielding yellow metal.
Meanwhile, an Israeli attack on Tehran and an Iranian missile strike raised doubts over the durability of the truce. This keeps geopolitical risk premium in play and might continue to offer some support to the Gold price. Moreover, the growing acceptance that the US central bank will resume its rate-cutting cycle as early as next month should cap any meaningful USD appreciation and limit the downside for the XAU/USD pair. Traders might also opt to wait for Powell’s second day of testimony on Tuesday and key US macro data scheduled during the latter half of the week.
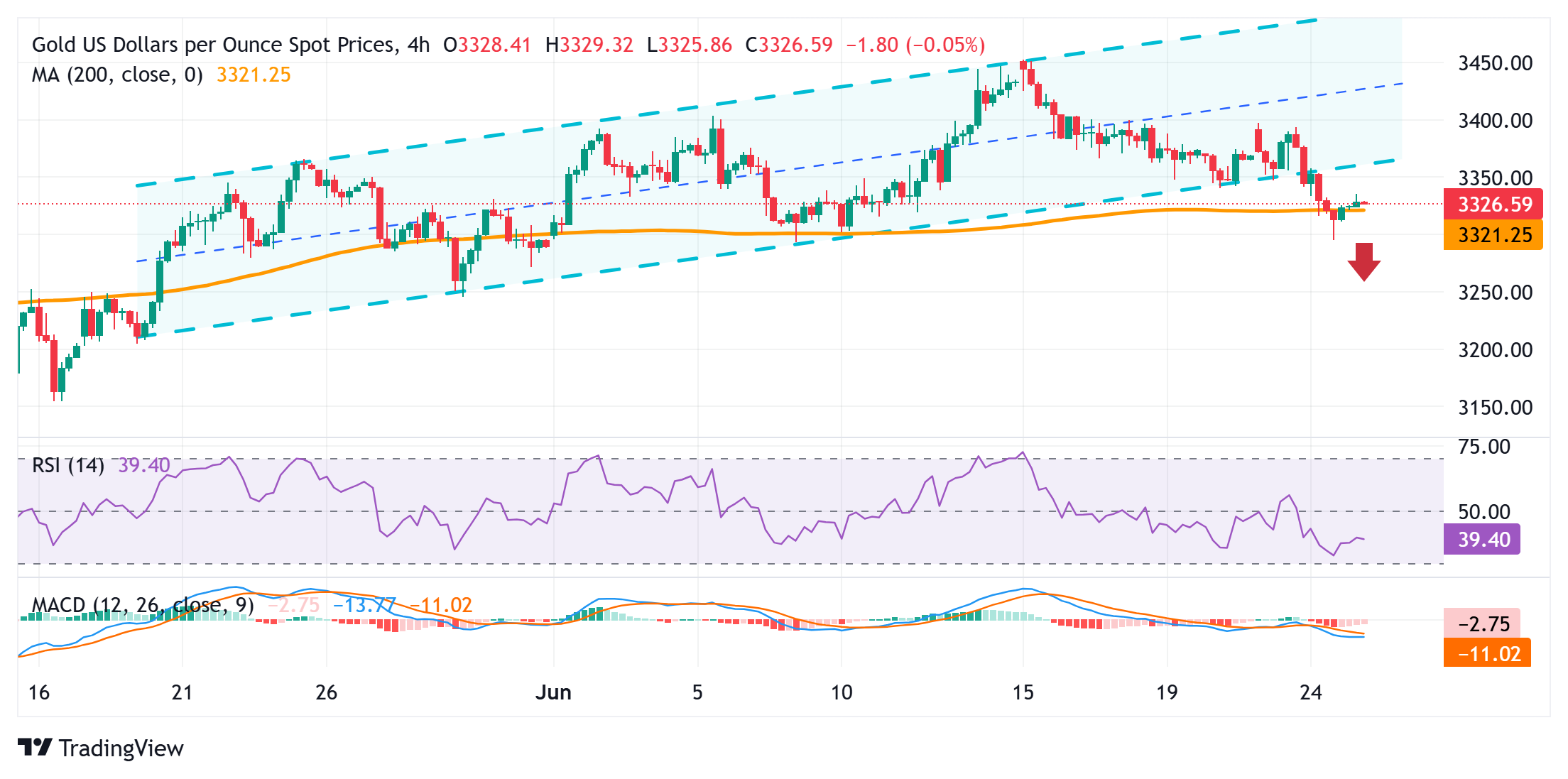
From a technical perspective, the overnight downfall confirmed a breakdown through a short-term ascending channel and favored bearish traders. Moreover, oscillators on daily/4-hour charts have started gaining negative traction and suggest that the path of least resistance for the Gold price is to the downside. Hence, any subsequent move up could be seen as a selling opportunity and remain capped near the trend-channel support breakpoint, around the $3,368-3,370 region. A sustained strength beyond, however, could allow the commodity to reclaim the $3,400 round figure.
On the flip side, bearish traders might now await acceptance below the $3,300 mark before placing fresh bets and positioning for a fall toward the $3,245 region. The downward trajectory could extend further and eventually drag the Gold price to the $3,210-$3,200 horizontal support en route to the $3,175 area.
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates.
When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money.
When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions.
The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system.
It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.